Brain
The brain is the primary organic data storage medium of animals with central nervous systems. Data is stored electrically in neurons, cells that process and transmit information through electrochemical signals. Signals move between neurons via specialized connections with other cells called synapses. Neurons can connect to each other to form neural networks that in turn are used to store data.
Data persistence
Short-term memory is volatile and stored as patterns of electrical activity. During sleep, short-term memories are consolidated into non-volatile long-term memory in the form of neural connections.
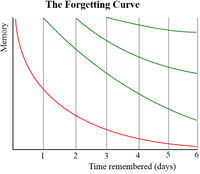
Information stored in brains is non-persistant and subject to being forgotten, through an automated garbage collection procedure. The rate of forgetting is determined by time interval since last memory recall, vividness and impact of the imprinted memory, and health state and age of the brain.